RICA Subtest 1
RICA Subtest 1 is the first section of the California Reading Instruction Competence Assessment, or RICA. It is designed to assess the knowledge and skills of aspiring teachers in the area of reading instruction. Read more below or click the button to get test prep now!

General Information
Overview
The RICA is an assessment used by the California Commission on Teacher Credentialing to measure a teacher‘s knowledge, skill, and ability in delivering effective reading instruction. It ensures that candidates for Multiple Subject Teaching Credentials and Education Specialist Instruction Credentials possess the necessary skills for providing such instruction.
The RICA Content Specifications are organized into five domains:
- Domain 1: Planning, Organizing, and Managing Reading Instruction Based on Ongoing Assessment
- Domain 2: Word Analysis
- Domain 3: Fluency
- Domain 4: Vocabulary, Academic Language, and Background Knowledge
- Domain 5: Comprehension
Types Of Assessments
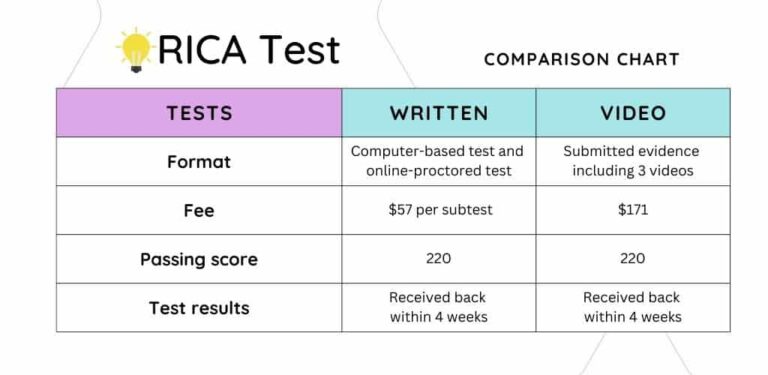
The RICA Test includes two different types of exams. There is the written examination and the video assessment.
The written exam is the most popular exam, and it includes 3 separate subtests which cover a variety of factors regarding reading instruction.
Have a look at the chart below to better understand the difference between RICA written exam and the video assessment.
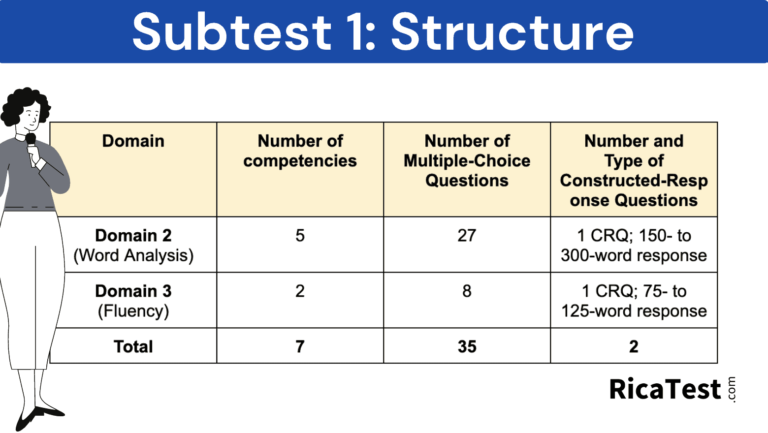
Subtest 1 Structure
As we can see from the image below, Rica Subtest 1 consists of domains 2, word analysis, and domain 3, fluency.
While taking Subtest 1, you will receive a total of 35 multiple-choice questions and two essay prompts. One essay prompt requires a written response of between 150 – 300 words, and one response requires a written response of between 75 – 125 words.
Subtest 1 Content Specifications
There’s a lot of information to remember to pass your RICA exam.
Important areas to focus on include the following:
Competency 3: Understand the role of phonological and phonemic awareness in reading development and how to develop students' phonological and phonemic awareness skills.
I. Introduction
- Overview of Domain 2 – Word Analysis
- Competency 3: Understanding the role of phonological and phonemic awareness in reading development and how to develop students’ phonological and phonemic awareness skills
II. Phonological and Phonemic Awareness
- Definition of phonological awareness (awareness of smaller units of language) and phonemic awareness (ability to distinguish individual phonemes in a word)
- Importance of phonological and phonemic awareness in reading development
III. Systematic, Explicit Instruction
- Research-based approach to instruction in phonological awareness, including phonemic awareness
- Examples of activities: detecting and identifying word boundaries, syllables, rhyming words, onset/rime; recognizing that words are made up of separate phonemes; blending, segmenting, deleting, and substituting phonemes
IV. Relationship Between Phonemic Awareness and Phonics Knowledge
- Connection between phonemic awareness and the development of phonics knowledge and skills (letter-sound correspondence, blending)
- Strategies for making explicit connections between phonemic awareness and letters (e.g. teaching phonemic awareness before instruction in letter knowledge)
V. Differentiated Instruction for All Learners
- Consideration of the needs of all learners in the classroom with respect to their development of phonological and phonemic awareness
- Examples of differentiated instruction for struggling readers, students with special needs, English learners, and advanced learners
VI. Assessment of Phonological and Phonemic Awareness
- Description and use of formal and informal assessments for different assessment purposes (entry-level, progress monitoring, summative)
- Ability to analyze and interpret results of assessments
- Use of results to plan effective instruction and interventions and determine whether standards have been met
Competency 4: Understand the role of concepts about print, letter recognition, and the alphabetic principle in reading development and how to develop students' knowledge and skills in these areas.
There’s a lot of information to remember to pass your RICA exam.
Important areas to focus on include the following:
I. Introduction
- Overview of Competency 4: Understanding the role of concepts about print, letter recognition, and the alphabetic principle in reading development and how to develop students’ knowledge and skills in these areas
II. Print Awareness
- Role of print awareness in early reading development
- Strategies for teaching concepts about print (relationship between spoken and written language, directionality of print, book-handling skills)
III. Letter Recognition
- Importance of accurate and rapid uppercase and lowercase letter recognition in reading development
- Research-based, systematic, explicit instruction in letter recognition, letter naming, and letter formation
- Factors to consider when planning instruction (visually and auditorily similar letters, practice in writing letters and words)
IV. Alphabetic Principle
- Role of the alphabetic principle in reading development (letter-sound correspondence, phonemic awareness, beginning decoding)
- Research-based, systematic, explicit instruction in the alphabetic principle
- Role of writing (phonetic spelling) in reinforcing understanding of the alphabetic principle and letter-sound correspondence
V. Differentiated Instruction for All Learners
- Consideration of the needs of all learners in the classroom with respect to concepts about print, letter recognition, and the alphabetic principle
- Examples of differentiated instruction for struggling readers, students with special needs, English learners, and advanced learners
VI. Assessment of Concepts About Print, Letter Recognition, and the Alphabetic Principle
- Description and use of formal and informal assessments for different assessment purposes (entry-level, progress monitoring, summative)
- Ability to analyze and interpret results of assessments
- Use of results to plan effective instruction and interventions and determine whether standards have been met
Competency 5: Understand important terminology and concepts involved in phonics instruction and recognize the role of phonics and sight words in reading development.
I. Role of phonics and sight words in reading development
- Accurate, automatic word identification
- Word recognition and reading fluency
- Word recognition and comprehension
II. Terminology and concepts related to phonics instruction
- Types of consonant sounds
- Common letter combinations
- Inflected morphological units
- Word patterns of increasing difficulty
- Syllable patterns and syllabication
- Phonetically irregular and decodable words
- Sight words until phonetic pattern is taught
III. Decoding and encoding as reciprocal skills
- Interrelationships between phonics and spelling/orthographic development
- Stages of spelling development and implications for instruction
- Writing activities and applying phonics knowledge in context
Competency 6: Understand how to develop students' phonics knowledge and skills and recognition of sight words to promote accurate word analysis that leads to automaticity in word recognition and contributes to spelling development.
I. Understanding the role of phonics and sight words in reading development
- Accurate and automatic word identification
- Role of word identification in word recognition and reading fluency and comprehension
II. Knowledge of research-based, systematic, explicit instruction in phonics and sight words
- Phonics and sight words appropriate for beginning-reading stage: sounding out and blending regular VC and CVC words, whole-word reading of single-syllable regular words and high-frequency irregular sight words, using decodable text, teaching students to spell VC and CVC words
- Phonics and sight words appropriate for more advanced stages of decoding: CVCC, CCVC, CVVC words with common regular letter combinations, regular CVCe words, less common phonics elements (e.g., kn, ph), decodable text, words with common inflected endings, spelling more complex orthographic patterns in single-syllable words and words with inflected endings
- Research-based, systematic, explicit instruction in sight words: high-frequency words that do and do not conform to regular phonics/spelling patterns, factors affecting sequence of instruction for specific sight words, explicit strategies for helping students master spelling of high-frequency sight words
III. Knowledge of how to address the full range of learners in the classroom with respect to their development of phonics skills, sight-word knowledge, and spelling of single-syllable words (Universal Access)
Competency 7: Understand the role of syllabic and structural analysis and orthographic knowledge in reading development and how to develop students' knowledge and skills in these areas to promote accurate word analysis that leads to automaticity in word recognition and contributes to spelling development.
- Recognize the role of phonics skills, sight-word knowledge, and syllabic and structural analysis and orthographic knowledge in accurate word analysis and automaticity in word recognition
- Demonstrate knowledge of systematic, explicit instruction in structural and syllabic analysis and spelling of multisyllabic words
- Recognize the relationship between orthographic knowledge and word analysis and demonstrate knowledge of systematic, explicit instruction in spelling/orthography
- Provide students with frequent opportunities to develop and extend their syllabic analysis skills, structural analysis skills, and orthographic knowledge in reading and writing
- Demonstrate knowledge of how to provide differentiated instruction for a range of learners in the areas of syllabic and structural analysis, orthographic knowledge, and decoding and spelling of multisyllabic words and words with more complex orthographic patterns or rules
- Demonstrate knowledge of how to use assessment data to inform instruction in syllabic and structural analysis, orthographic knowledge, and decoding and spelling of multisyllabic words and words with more complex orthographic patterns or rules
Competency 8: Understand the role of fluency in reading development and factors that affect students' development of fluency.
- Role of fluency in reading development
- Indicators of reading fluency: accuracy, rate, prosody
- Interrelationships among word analysis skills, fluency, vocabulary, academic language, background knowledge, and comprehension
- Factors that disrupt fluency
- Role of decodable text in promoting fluent reading
- Importance of systematic, explicit instruction in promoting fluency development
- Limitations of using independent silent reading to increase automaticity
- Factors that make independent silent reading more effective in supporting fluency development
Competency 9: Understand how to promote students' fluency development.
- Components of effective fluency instruction
- Research-based, systematic, explicit instruction in fluency
- Strategies for building fluency with respect to accuracy
- Strategies for building fluency with respect to rate
- Strategies for building fluency with respect to prosody
- Differentiated fluency instruction for struggling readers and students with reading difficulties or disabilities
- Differentiated fluency instruction for students with special needs
- Differentiated fluency instruction for English Learners and speakers of nonstandard English
- Differentiated fluency instruction for advanced learners
- Importance of ongoing assessment of students’ fluency development
- Strategies for reinforcing and reinforcing fluency skills and knowledge
- Use of authentic texts to build fluency
- Use of technology to support fluency development
